The key difference between relative dating and radiometric dating is that the dating cannot provide actual numerical dates whereas the radiometric dating can provide actual numerical dates. Relative dating and radiometric dating are two types of parameters that we use to describe the age of geological features and to determine the relative order of past events. Here, we are talking about millions and billions of years.
Let us discuss more details about these terms.
- What is Radiometric Dating?.
- Difference between relative dating and radiometric dating.
- Difference Between Relative Dating and Radiometric Dating l Relative Dating vs Radiometric Dating.
- speed dating nyc 20-30?
- Explain the difference between relative dating and radiometric dating.?.
- Relative Dating vs. Absolute Dating: What's the Difference?.
- Relative Dating vs. Absolute Dating: What’s the Difference? – Difference Wiki.
Overview and Key Difference 2. What is Relative Dating 3.
What is Relative Dating?
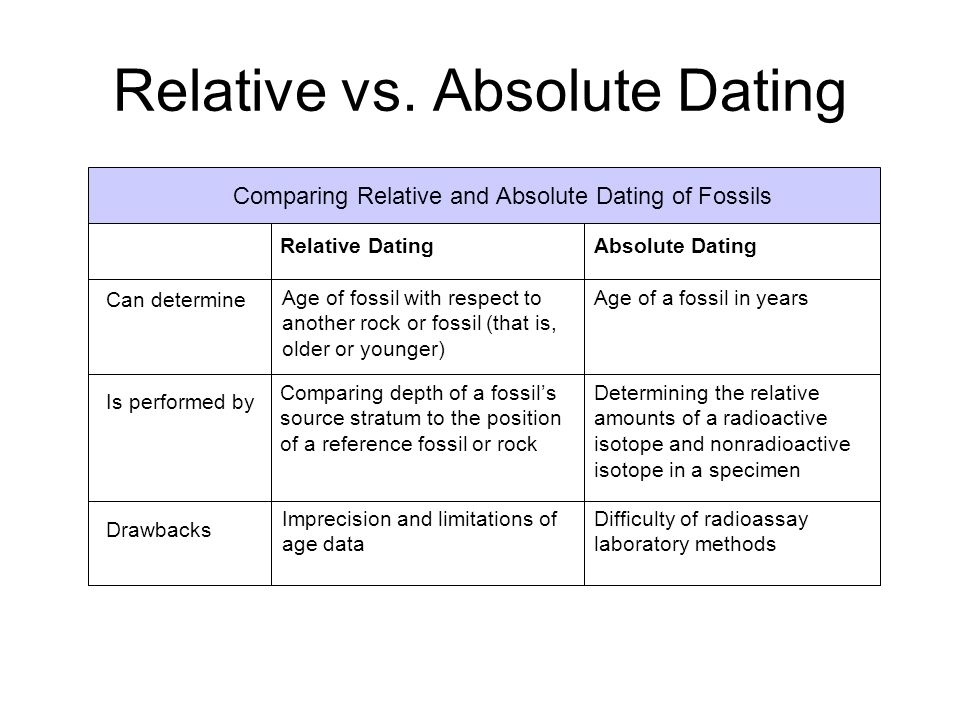
What is Radiometric Dating 4. Relative dating is determining the relative order of past events via determining the approximate age of geological features. The method of reading this order is called stratigraphy. This does not give the actual numerical dates.
Fossils are the key to determine the relative dating in sedimentary rocks. A sedimentary rock contains different layers being the oldest at the bottom and youngest at the top. With time, different organisms appear and flourish leaving their fossils in sedimentary rocks.
explain the difference between relative dating and radiometric dating.? | Yahoo Answers
Therefore, we can identify the sequence of different lives on earth via relative dating. Relative techniques are of great help in such types of sediments. The following are the major methods of relative dating. The oldest dating method which studies the successive placement of layers.
It is based on the concept that the lowest layer is the oldest and the topmost layer is the youngest. An extended version of stratigraphy where the faunal deposits are used to establish dating. Faunal deposits include remains and fossils of dead animals. This method compares the age of remains or fossils found in a layer with the ones found in other layers. The comparison helps establish the relative age of these remains. Bones from fossils absorb fluorine from the groundwater. The amount of fluorine absorbed indicates how long the fossil has been buried in the sediments.
This technique solely depends on the traces of radioactive isotopes found in fossils. The rate of decay of these elements helps determine their age, and in turn the age of the rocks. Physical structure of living beings depends on the protein content in their bodies. The changes in this content help determine the relative age of these fossils.
Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off
Each tree has growth rings in its trunk. This technique dates the time period during which these rings were formed. It determines the period during which certain object was last subjected to heat. It is based on the concept that heated objects absorb light, and emit electrons.
The emissions are measured to compute the age. Differentiation Using a Venn Diagram. A Venn diagram depicts both dating methods as two individual sets.
- Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off.
- famous dating site in america?
- Navigation menu.
- lesbian dating online philippines?
- plenty of fish singles dating site?
The area of intersection of both sets depicts the functions common to both. Take a look at the diagram to understand their common functions. When we observe the intersection in this diagram depicting these two dating techniques, we can conclude that they both have two things in common: Provide an idea of the sequence in which events have occurred.
