Gamma rays are produced when a nucleus undergoes a transition from a higher to a lower energy state, similar to how a photon is produced by an electronic transition from a higher to a lower energy level. Due to the much larger energy differences between nuclear energy shells, gamma rays emanating from a nucleus have energies that are typically millions of times larger than electromagnetic radiation emanating from electronic transitions. A balanced chemical reaction equation reflects the fact that during a chemical reaction, bonds break and form, and atoms are rearranged, but the total numbers of atoms of each element are conserved and do not change.
A balanced nuclear reaction equation indicates that there is a rearrangement during a nuclear reaction, but of subatomic particles rather than atoms. Nuclear reactions also follow conservation laws, and they are balanced in two ways:. If the atomic number and the mass number of all but one of the particles in a nuclear reaction are known, we can identify the particle by balancing the reaction. Balancing Equations for Nuclear Reactions.
- Who's it for?.
- Nuclear Chemistry & Radioactive Decay: Help and Review - Videos & Lessons | pcppk.com!
- Radioactive Dating.
- Radiocarbon Dating - Chemistry LibreTexts!
- Radioactive Dating!
Identify the new nuclide produced. Because the sum of the mass numbers of the reactants must equal the sum of the mass numbers of the products:. Check the periodic table: What is the equation for this reaction? Following are the equations of several nuclear reactions that have important roles in the history of nuclear chemistry:.
Following the somewhat serendipitous discovery of radioactivity by Becquerel, many prominent scientists began to investigate this new, intriguing phenomenon. During the beginning of the twentieth century, many radioactive substances were discovered, the properties of radiation were investigated and quantified, and a solid understanding of radiation and nuclear decay was developed. The alpha particle removes two protons green and two neutrons gray from the uranium nucleus. Although the radioactive decay of a nucleus is too small to see with the naked eye, we can indirectly view radioactive decay in an environment called a cloud chamber.
How to Build a Cloud Chamber! We classify different types of radioactive decay by the radiation produced. Alpha particles, which are attracted to the negative plate and deflected by a relatively small amount, must be positively charged and relatively massive. Beta particles, which are attracted to the positive plate and deflected a relatively large amount, must be negatively charged and relatively light.
Gamma rays, which are unaffected by the electric field, must be uncharged. The beta particle electron emitted is from the atomic nucleus and is not one of the electrons surrounding the nucleus.
Navigation menu
Such nuclei lie above the band of stability. Emission of an electron does not change the mass number of the nuclide but does increase the number of its protons and decrease the number of its neutrons. Oxygen is an example of a nuclide that undergoes positron emission:. Positron emission is observed for nuclides in which the n: These nuclides lie below the band of stability.
3.1: Nuclear Chemistry and Radioactive Decay
Positron decay is the conversion of a proton into a neutron with the emission of a positron. For example, potassium undergoes electron capture:. Electron capture occurs when an inner shell electron combines with a proton and is converted into a neutron. The loss of an inner shell electron leaves a vacancy that will be filled by one of the outer electrons. As the outer electron drops into the vacancy, it will emit energy. In most cases, the energy emitted will be in the form of an X-ray. Electron capture has the same effect on the nucleus as does positron emission: The atomic number is decreased by one and the mass number does not change.
- dating single parents perth.
- Radiocarbon Dating.
- .
- Radiometric dating - Wikipedia!
- filipino dating kisses international.
- drug dealers dating.
This increases the n: Whether electron capture or positron emission occurs is difficult to predict. The choice is primarily due to kinetic factors, with the one requiring the smaller activation energy being the one more likely to occur. This table summarizes the type, nuclear equation, representation, and any changes in the mass or atomic numbers for various types of decay.
Radiometric dating
The naturally occurring radioactive isotopes of the heaviest elements fall into chains of successive disintegrations, or decays, and all the species in one chain constitute a radioactive family, or radioactive decay series. Three of these series include most of the naturally radioactive elements of the periodic table. They are the uranium series, the actinide series, and the thorium series.
The neptunium series is a fourth series, which is no longer significant on the earth because of the short half-lives of the species involved.
Nuclear Chemistry and Radioactive Decay - Chemistry LibreTexts
In all three series, the end-product is a stable isotope of lead. The neptunium series, previously thought to terminate with bismuth, terminates with thallium Uranium undergoes a radioactive decay series consisting of 14 separate steps before producing stable lead Radioactive decay follows first-order kinetics. Since first-order reactions have already been covered in detail in the kinetics chapter, we will now apply those concepts to nuclear decay reactions.
For example, cobalt, an isotope that emits gamma rays used to treat cancer, has a half-life of 5. Note that for a given substance, the intensity of radiation that it produces is directly proportional to the rate of decay of the substance and the amount of the substance. This is as expected for a process following first-order kinetics.
Thus, a cobalt source that is used for cancer treatment must be replaced regularly to continue to be effective. For cobalt, which has a half-life of 5. Since nuclear decay follows first-order kinetics, we can adapt the mathematical relationships used for first-order chemical reactions. We generally substitute the number of nuclei, N , for the concentration. If the rate is stated in nuclear decays per second, we refer to it as the activity of the radioactive sample.
The rate for radioactive decay is:. The first-order equations relating amount, N , and time are:. We will not concern ourselves with the calculation of half-life in this course. Because each nuclide has a specific number of nucleons, a particular balance of repulsion and attraction, and its own degree of stability, the half-lives of radioactive nuclides vary widely.
This process is radiometric dating and has been responsible for many breakthrough scientific discoveries about the geological history of the earth, the evolution of life, and the history of human civilization. We will explore some of the most common types of radioactive dating and how the particular isotopes work for each type. The radioactivity of carbon provides a method for dating objects that were a part of a living organism. This method of radiometric dating, which is also called radiocarbon dating or carbon dating, is accurate for dating carbon-containing substances that are up to about 30, years old, and can provide reasonably accurate dates up to a maximum of about 50, years old.
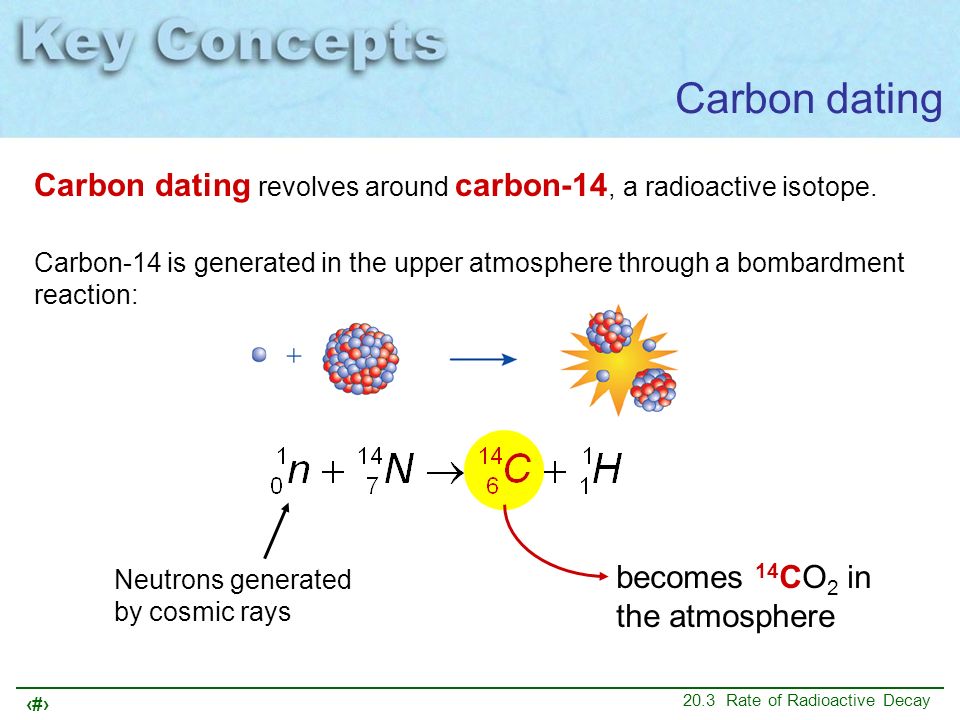
Naturally occurring carbon consists of three isotopes: Carbon forms in the upper atmosphere by the reaction of nitrogen atoms with neutrons from cosmic rays in space:. They found a form, isotope, of Carbon that contained 8 neutrons and 6 protons. Using this finding Willard Libby and his team at the University of Chicago proposed that Carbon was unstable and underwent a total of 14 disintegrations per minute per gram.
Using this hypothesis, the initial half-life he determined was give or take 30 years.
How it works:
Although it may be seen as outdated, many labs still use Libby's half-life in order to stay consistent in publications and calculations within the laboratory. From the discovery of Carbon to radiocarbon dating of fossils, we can see what an essential role Carbon has played and continues to play in our lives today. The entire process of Radiocarbon dating depends on the decay of carbon This process begins when an organism is no longer able to exchange Carbon with their environment.
Carbon is first formed when cosmic rays in the atmosphere allow for excess neutrons to be produced, which then react with Nitrogen to produce a constantly replenishing supply of carbon to exchange with organisms. Skills to Develop Identify the age of materials that can be approximately determined using radiocarbon dating.
The Carbon cycle Radiocarbon dating usually referred to simply as carbon dating is a radiometric dating method. History The technique of radiocarbon dating was developed by Willard Libby and his colleagues at the University of Chicago in Summary The entire process of Radiocarbon dating depends on the decay of carbon Carbon dating can be used to estimate the age of carbon-bearing materials up to about 58, to 62, years old. The carbon isotope would vanish from Earth's atmosphere in less than a million years were it not for the constant influx of cosmic rays interacting with atmospheric nitrogen.
One of the most frequent uses of radiocarbon dating is to estimate the age of organic remains from archeological sites. A Chronological Tool for the Recent Past. The slope of the curve then gives the time interval. Radioactive Dating Because the radioactive half-life of a given radioisotope is not affected by temperature, physical or chemical state, or any other influence of the environment outside the nucleus save direct particle interactions with the nucleus, then radioactive samples continue to decay at a predictable rate and can be used as a clock.
For geologic dating, where the time span is on the order of the age of the earth and the methods use the clocks in the rocks , there are two main uncertainties in the dating process: What was the amount of the daughter element when the rocks were formed?
Have any of the parent or daughter atoms been added or removed during the process? The requirement of keeping the same number of nuclei gives and the radioactive decay relationship is The elapsed time is then but with the use of the first expression above can be expressed in terms of the present concentrations of the parent and daughter isotopes. The requirement on the populations is now Fortunately for radioactive dating processes, additional information is available in the form of other isotopes of the elements involved in the radioactive process. If there is another isotope of the daugther element D' which is presumed to be constant throughout the process, then the population requirement can be expressed in terms of the ratios We can be reasonably confident that the isotope D' is contant if it is not radioactive not part of one of the natural radioactive series.
The age can then be calculated from that slope as follows: Index Reference Krane Sec 6.
