William Compston, et al. Rama Murthy, et al.
First Rock Dating Experiment Performed on Mars
As you can see, the age of the same rock measured by different scientists using different techniques varied widely. Which age is correct? Sample was dated by five different sources with nineteen different results. Here is how one of those sources tried to spin the results. The 40 K- 40 Ar ages are for No. Comparison of mineral and rock data demonstrates gas loss. The plagioclase for No. The concordance of He and Ar ages must be fortuitous. The maximum age is equal to the Rb-Sr age, and the general pattern is compatible with the Sr results.
Seven crystalline rock samples returned by Apollo 11 have been analyzed in detail by means of the 40 Ar- 39 Ar dating technique. Potassium-argon ages, corrected for the effects of this loss, cluster relatively closely around the value of 3. Most of the vulcanism associated with the formation of the Mare Tranquillitatis presumably occurred around 3. A major cause of the escape of gas from lunar rock is probably the impact event which ejected the rock from its place of origin to its place of discovery. One technique, potassium-argon dating, determines the age of a rock sample by measuring how much argon gas it contains.
Over time, atoms of the radioactive form of potassium—an isotope called potassium—will decay within a rock to spontaneously form stable atoms of argon This decay occurs at a known rate, so by determining the amount of argon in a sample, researchers can calculate the sample's age. Although the potassium-argon method has been used to date rocks on Earth for many decades, these types of measurements require sophisticated lab equipment that could not easily be transported and used on another planet. Farley had the idea of performing the experiment on Mars using the SAM instrument.
There, the sample was heated to temperatures high enough that the gasses within the rock were released and could be analyzed by an onboard mass spectrometer.
- The Age of the Moon?
- dating coach south carolina?
- Clocks in the Rocks;
- Moon rock - Wikipedia?
- Lunar radioactivity;
- .
- free match making of kundli in hindi?
Farley and his colleagues determined the age of the mudstone to be about 3. Indeed, prior to Curiosity's geochronology experiment, researchers using the "crater counting" method had estimated the age of Gale Crater and its surroundings to be between 3. Crater counting relies on the simple fact that planetary surfaces are repeatedly bombarded with objects that scar their surface with impact craters; a surface with many impact craters is presumed to be older than one with fewer craters.
The Age of the Moon
Although this method is simple, it has large uncertainties. The researchers do, however, acknowledge that there is some uncertainty in their measurement.
- taunton speed dating?
- dating houston singles?
- Moon Rocks dated past billion years?? : Creationism • Rational Skepticism Forum?
- Clocks in the Rocks?
- The Details.
- arrow irelands leading dating agency?
- .
- .
- lala dating?
- First Rock Dating Experiment Performed on Mars | Caltech?
- .
- ;
- ?
- speed dating associations paris?
One reason is that mudstone is a sedimentary rock—formed in layers over a span of millions of years from material that eroded off of the crater walls—and thus the age of the sample drilled by Curiosity really represents the combined age of those bits and pieces. So while the mudstone indicates the existence of an ancient lake—and a habitable environment some time in the planet's distant past—neither crater counting nor potassium-argon dating can directly determine exactly when this was. To provide an answer for how the geology of Yellowknife Bay has changed over time, Farley and his colleagues also designed an experiment using a method called surface exposure dating.
Cosmic rays can only penetrate about two to three meters below the surface, so the abundance of cosmic-ray-debris isotopes in rock indicates how long that rock has been on the surface. Using the SAM mass spectrometer to measure the abundance of three isotopes that result from cosmic-ray bombardment—helium-3, neon, and argon—Farley and his colleagues calculated that the mudstone at Yellowknife Bay has been exposed at the surface for about 80 million years.
Some of the decays which are useful for dating, with their half-lives and decay constants are:. The half-life is for the parent isotope and so includes both decays.
Some decays with shorter half-lives are also useful. Of these, the 14 C is unique and used in carbon dating. Note that the decay constant scale in the table below was kept the same as the table above for comparison.
Navigation menu
Parent isotope radioactive Daughter isotope stable Half-life y Decay constant 10 yr -1 10 Be 10 B 1. Of those isotopes, are stable and 70 are radioactive. Eighteen of the radioactive elements have long enough half-lives to have survived since the beginning of the solar system. The table above includes the main isotopes used for age studies.
The natural radioactive series which involve lead as a daughter element do offer a mechanism to test the assumptions. Common lead contains a mixture of four isotopes. Lead , which is not produced by radioactive decay provides a measure of what was "original" lead. It is observed that for most minerals, the proportions of the lead isotopes is very nearly constant, so the lead can be used to project the original quantities of lead and lead Lead is the final stable product of the Thorium series , so is not used in uranium-lead dating.
The two uranium-lead dates obtained from U and U have different half-lives, so if the date obtained from the two decays are in agreement, this adds confidence to the date.
Lunar radioactivity - RationalWiki
They are not always the same, so some uncertainties arise in these processes. There are powerful rationales for using lead isotopes as indicative of concentrations at the point when the lead-containing mineral was in the molten state. Since the isotopes of lead are chemically identical, any processes that brought lead into the mineral would be completely indiscriminate about which isotope was brought in. The forming mineral will incorporate lead, lead and lead at the ratio at which they are found at that location at the time of formation.
Any departure from the original relative concentrations of lead and lead relative to lead could then be attributed to radioactive decay. This approach is generally considered to be the most precise for determining the age of the Earth. Potassium-Argon dating has the advantage that the argon is an inert gas that does not react chemically and would not be expected to be included in the solidification of a rock, so any found inside a rock is very likely the result of radioactive decay of potassium.
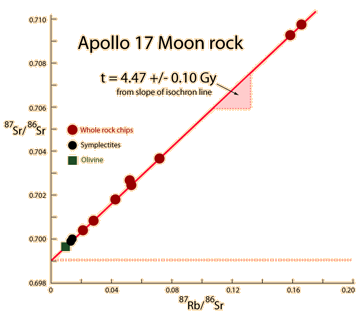
Since the argon will escape if the rock is melted, the dates obtained are to the last molten time for the rock. The radioactive transition which produces the argon is electron capture. The rubidium-strontium pair is often used for dating and has a non-radiogenic isotope, strontium, which can be used as a check on original concentrations of the isotopes.
This process is often used along with potassium-argon dating on the same rocks. The ratios of rubidium and strontium to the strontium found in different parts of a rock sample can be plotted against each other in a graph called an isochron which should be a straight line.
