How the Administrations Overtime Rule Could Cost Workers More Than They Gain Including Flexibility and Income Security
Some exceptions apply under special circumstances to police and firefighters and to employees of hospitals and nursing homes. New York’s state overtime law requires overtime pay at a rate of 1.5 times the state minimum wage for hours worked beyond 40 for these FLSA-exempt individuals. Minnesota’s state overtime law requires overtime pay for hours worked beyond 48 in a workweek. Because the federal law is 40 hours, follow the FLSA if you’re covered under it. Unless specifically exempted, employees covered by the Act must receive overtime pay for hours worked in excess of 40 in a workweek at a rate not less than time and one-half their regular rates of pay. The Act does not require overtime pay for work on Saturdays, Sundays, holidays, or regular days of rest, as such.
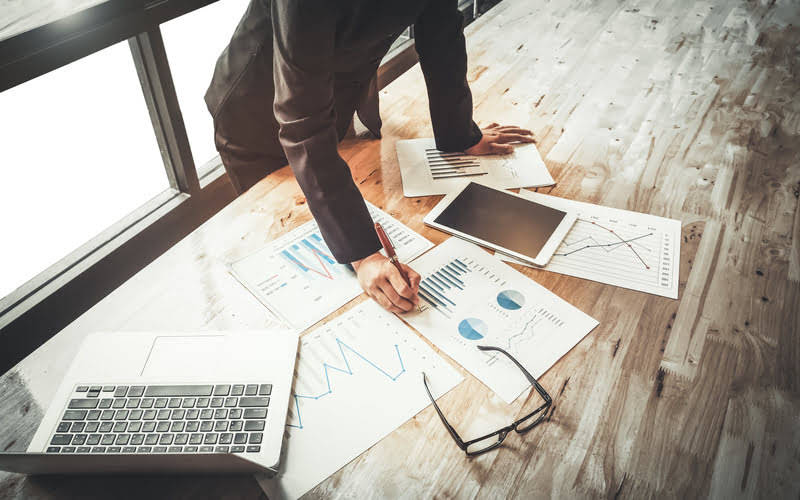

Since compensatory time is a liability, operating unit heads may set policies governing its accrual. For instance, they can decide whether – or not – FLSA exempt employees above the GS-10 level will be given compensatory time for overtime hours worked. They can also allow lower grade employees to choose compensatory time instead of overtime. They may also set limits on how much compensatory time employees may earn. If you are required to work more that 8 hours a day or more than the standard 40-hour workweek, you can expect to be compensated for the extra time, either by payment at an overtime rate, or by time off on an hour-for-hour basis (known as compensatory time off). The law expands the definition of a covered employee, uses a different regular rate of pay calculation, extends the statute of limitations to three years, and may result in more severe damages for employers who fail to pay overtime.
Withholding of Wages
However, Michigan’s overtime law applies to employers with two or more employees. However, the state does consider hours worked beyond eight in a workday overtime if the work is performed on a State or county public works construction project. And, some state laws are stricter, triggering how to calculate overtime pay if an employee works beyond a certain number of hours in a day.
Today, “free time” is something you’re expected to surrender to your boss. And the pandemic-inspired work-from-home “revolution” isn’t make things any better. In fact, according to ADP, those working from home report putting in even more unpaid overtime than their traditional workplace counterparts. Having too few education options can restrict opportunities for successful careers. Instead of mandating higher salaries that cost workers more than their wage gains, policymakers should open doors to rising incomes and flexible work opportunities. If you are eligible, the Fair Labor Standards Act gives you the right to earn overtime pay.
Overtime Pay
Overtime pay is the extra money you earn for working beyond your regularly scheduled working hours. It’s meant to reward your extra effort and is
an important aspect of many employees’ compensation packages. Besides all of that, let’s take a look at the formal overtime definition. Overtime is the amount of time that an employee works beyond regular working hours. Or, in other words – overtime refers to any hours that someone worked exceeding their typically scheduled work time. Moreover, the term overtime is often used to name the payment received for extra working hours.
- In fact, according to ADP, those working from home report putting in even more unpaid overtime than their traditional workplace counterparts.
- Of course, this money would have to come from somewhere, and often that somewhere is reflected in higher prices for consumers.
- Expanded overtime periods would give workers greater flexibility to request changes to their weekly schedules while continuing to work for the same total number of hours.
- The proposed rule subjects U.S. territories to the same overtime thresholds as the U.S. mainland (with the exception of American Samoa, to which it applies a lower overtime threshold).
- In contrast to periodic updates as specified by Congress, the proposed rule would establish automatic updates to the threshold in future years.REF The proposal would also apply the increased overtime threshold to employees in Puerto Rico, Guam, the U.S.
- Thus, some employers could prevent compensation increases while maintaining the same output level by reducing workers’ hours and using more part-time workers.
That’s on top of the 2,500 transit officers already working in the system in the NYPD’s $250 million transit bureau, he said. The new spending was part of a push by Mayor Eric Adams and Gov. Kathy Hochul to reduce crime and crack down on New Yorkers sleeping in the transit system – in part by flooding the subways with uniformed NYPD officers working overtime shifts. In the meantime, the next step is for OPM to issue updated pay tables. The 2024 pay tables have been published on OPM’s website, and can be viewed here. Let’s take a look at what the overtime entitlements are in the U.S. and how they can vary by state… Most employers in West Virginia are subject to the Fair Labor Standards Act.
Formulas for overtime pay
Whatever the limit is (some laws contain other thresholds), the employer should compensate for each hour exceeding the normal threshold. Keep reading to learn helpful information about overtime rules and https://www.bookstime.com/ according to labor law regulations. What is more, you will discover what is time and a half pay, who is an exempt employee is, and some examples of exempt jobs. Department of Labor issued new regulations around pay for exempt employees that make more employees eligible for overtime pay. If you’re under the age of 45, you may have no idea that overtime pay is even a thing.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!